Fc epsilon RI-mediated chloride uptake by rat mast cells: modulation by chloride transport inhibitors in relation to histamine secretion.
A C Redrup, J C Foreman, N A Hayes, F L Pearce
Index: Br. J. Pharmacol. 122(6) , 1188-94, (1997)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
1. We have examined the role of extracellular chloride in the mast cell secretion process. The immunologically-directed ligand, antibody to IgE (anti-IgE) required extracellular chloride ions for optimum secretion from rat peritoneal mast cells. In contrast, replacement of extracellular chloride did not alter the mast cell secretory response to compound 48/80, calcium ionophore A23187 or substance P. 2. Anti-IgE-stimulation of mast cells evoked a significant uptake of chloride ions compared to non-stimulated cells. The magnitude of chloride uptake correlated with the magnitude of stimulated histamine secretion. 3. Compound 48/80, substance P and A23187 did not alter the rate of chloride ion uptake, although these agents caused significant histamine secretion. 4. The Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransport inhibitor, furosemide, reduced the rate of anti-IgE-stimulated chloride uptake at a relatively high concentration (700 microM). However, the more potent Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransport inhibitors, bumetanide (100 microM) and piretanide (100 microM) had no effect on the stimulated chloride uptake. 5. Furosemide inhibited anti-IgE-induced histamine secretion, bumetanide potentiated the response and piretanide had no effect. This suggests that their respective action on histamine secretion are unrelated to inhibition of the Na+/K+/2Cl- carrier. 6. The chloride channel blocker, 5-nitro-2-((3-phenylpropyl)-amino)-benzoic acid (NPPB), reduced both anti-IgE-stimulated chloride uptake and the corresponding histamine secretion in a dose-dependent manner. The magnitude of the inhibitory action of the drug on these two cellular processes was comparable, implying that chloride channel activity is related to the mechanism of histamine secretion. 7. It is concluded that chloride uptake has a role in the control of Fc epsilon RI-mediated histamine secretion from rodent mast cells.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
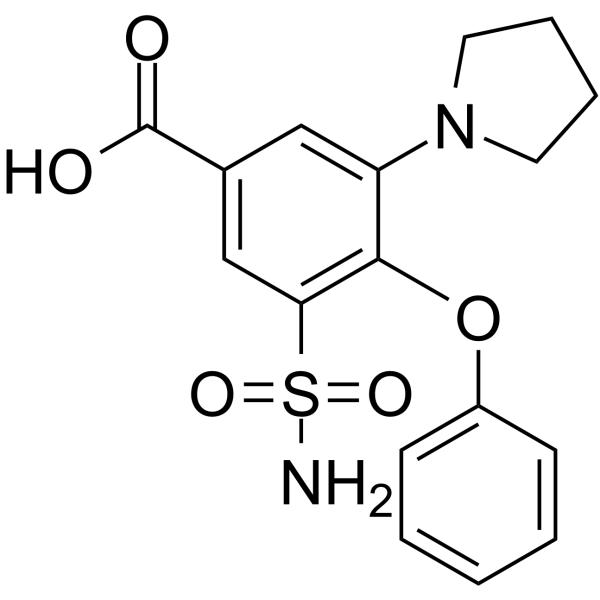 |
Piretanide
CAS:55837-27-9 |
C17H18N2O5S |
|
Role of EDHF in the vasodilatory effect of loop diuretics in...
2000-11-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 131(6) , 1211-9, (2000)] |
|
Modulation of chloride, potassium and bicarbonate transport ...
1999-01-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 126(1) , 269-79, (1999)] |
|
Usefulness of piretanide plus ramipril for systemic hyperten...
1993-09-15 [Am. J. Cardiol. 72(9) , 666-71, (1993)] |
|
Increased (Na+K+Cl) cotransport in rat arterial smooth muscl...
1999-01-01 [J. Vasc. Res. 36(6) , 492-501, (1999)] |
|
Stability-indicating methods for the determination of pireta...
2005-10-04 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 39(5) , 871-6, (2005)] |