Studies on the removal of Lissamine Green B from clays and soil in comparison with contemporary approaches.
Dean F Martin, Neel Nabar
Index: J. Environ. Sci. Health. A. Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 47(2) , 260-6, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A combination of Fenton's reagent with electrochemistry has been demonstrated to be a efficient method for removing a dye (Lissamine Green B) from clays (kaolin, montmorillonite) and soil. The two-step approach described here involved quantitative extraction with hot water, followed by quantitative removal of the Lissamine Green dye by column chromatography using Octolig®. The advantage of this procedure is success without the need for Fenton reagents or electricity. A disadvantage is the process would not work with polycyclic hydrocarbons such as phenanthrene, though the electro-Fenton degradation does.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
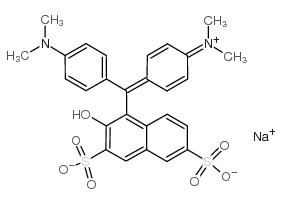 |
Green S
CAS:3087-16-9 |
C27H25N2NaO7S2 |
|
Comparative Genomics of Listeria Sensu Lato: Genus-Wide Diff...
2015-08-01 [Genome Biol. Evol. 7 , 2154-72, (2015)] |
|
Electro-Fenton decolourisation of dyes in an airlift continu...
2013-04-01 [Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 20(4) , 2252-61, (2013)] |
|
Decolourisation of dyes under electro-Fenton process using F...
2012-04-30 [J. Hazard. Mater. 213-214 , 369-77, (2012)] |
|
[Substances for staining biological tissues: use of dyes in ...
2005-04-01 [Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 222(4) , 309-11, (2005)] |
|
PCR assessment of HSV-1 corneal infection in animals treated...
2000-07-01 [Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 41(8) , 2096-102, (2000)] |