The role of irreversible EGFR inhibitors in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: overcoming resistance to reversible EGFR inhibitors.
Chandra P Belani
Index: Cancer Invest. 28(4) , 413-23, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Reversible epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors are often used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer following failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy. While these agents are active in a subset of patients, most develop resistance and progress within the course of 1 year. In nearly half of the cases, acquired resistance is caused by a secondary epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation. Irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors are an emerging class of agents that may have the potential to overcome and prevent the emergence of such mutation-related resistance.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
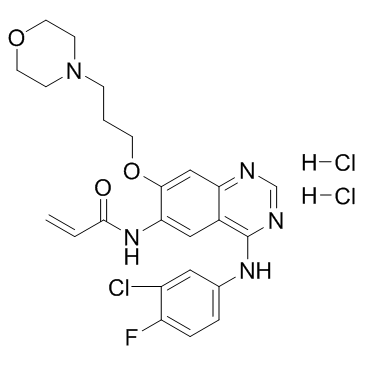 |
Canertinib dihydrochloride
CAS:289499-45-2 |
C24H27Cl3FN5O3 |
|
Breast cancer cells can switch between estrogen receptor alp...
2010-06-01 [Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 121(3) , 601-13, (2010)] |
|
A multivariate model of ErbB network composition predicts ov...
2012-01-01 [Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109(1) , 213-24, (2012)] |
|
Differential action of small molecule HER kinase inhibitors ...
2012-07-01 [Int. J. Cancer 131(1) , 244-52, (2012)] |
|
Clinical stage EGFR inhibitors irreversibly alkylate Bmx kin...
2008-11-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18(22) , 5916-9, (2008)] |
|
The pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor canertinib i...
2010-02-26 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 393(1) , 6-10, (2010)] |