Effect of the herbicide 4-CPA on human erythrocyte antioxidant enzymes in vitro.
Y Alicigüzel, S Ozdem, A Y Demir, F Unal, D Kumbul, S S Ozdem, G Perry, M A Smith
Index: Redox Rep. 6(3) , 153-4, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To investigate the possible role of oxygen free radicals and oxidant stress in the toxic effects of phenoxyherbicides, we studied the in vitro effect of 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (4-CPA) on various human erythrocyte antioxidant enzymes, namely glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, catalase, selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase and Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase. 4-CPA added in a dose of 1 ppm to human erythrocytes for 1 h caused a significant reduction in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (P <0.001) and catalase (P <0.001) activities, but did not significantly affect the activities of other enzymes. Such selective inactivation of specific erythrocyte antioxidant enzymes may play a role in the toxic effects of phenoxyherbicides.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
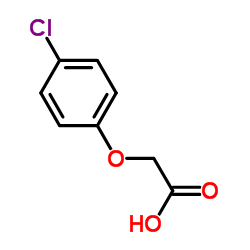 |
4-CPA
CAS:122-88-3 |
C8H7ClO3 |
|
Phenoxy herbicides and fibrates potently inhibit the human c...
2009-11-12 [J. Med. Chem. 52 , 6931-5, (2009)] |
|
Amphiphilic blockers punch through a mutant CLC-0 pore.
2009-01-01 [J. Gen. Physiol. 133(1) , 59-68, (2009)] |
|
Molecular modeling of p-chlorophenoxyacetic acid binding to ...
2003-05-13 [Biochemistry 42(18) , 5176-85, (2003)] |
|
Chlorophenoxyacetic acid and chloropyridylphenylurea acceler...
2011-06-15 [J. Plant Physiol. 168 , 920-926, (2011)] |
|
Chromatographic analysis of 1,3-bis(dimethylamino)isopropyl ...
1992-01-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 10(2-3) , 213-7, (1992)] |