Procaterol inhibits rhinovirus infection in primary cultures of human tracheal epithelial cells.
Mutsuo Yamaya, Hidekazu Nishimura, Yukimasa Hatachi, Motoki Yoshida, Hidenori Fujiwara, Masanori Asada, Katsutoshi Nakayama, Hiroyasu Yasuda, Xue Deng, Takahiko Sasaki, Hiroshi Kubo, Ryoichi Nagatomi
Index: Eur. J. Pharmacol. 650(1) , 431-44, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
β(2) agonists reduce the frequency of exacerbations in patients with bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease caused by respiratory virus infection. β(2) agonists reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. However, the inhibitory effects of β(2) agonists on the infection of rhinovirus, the major cause of exacerbations, have not been well studied. To examine the effects of a β(2) agonist, procaterol, on rhinovirus infection and rhinovirus infection-induced airway inflammation, human tracheal epithelial cells were infected with a major group rhinovirus, type 14 rhinovirus. Rhinovirus infection increased viral titers and the content of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1β and interlukin-6, in supernatant fluids and rhinovirus RNA in the cells. Procaterol reduced rhinovirus titers and RNA, cytokine concentrations, and susceptibility to rhinovirus infection. Procaterol reduced the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), the receptor for type 14 rhinovirus, and the number of acidic endosomes in the cells from which rhinovirus RNA enters into the cytoplasm. Procaterol inhibited the activation of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) proteins including p50 and p65 in the nuclear extracts, while it increased the cytosolic amount of the inhibitory kappa B-α and intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels. A selective β(2)-adrenergic receptor antagonist ICI 118551 [erythro-dl-1-(7-methylindan-4-yloxy)-3-isopropylaminobutan-2-ol] reversed the inhibitory effects of procaterol on rhinovirus titers and RNA, susceptibility to rhinovirus infection, pro-inflammatory cytokines production, ICAM-1 expression, acidic endosomes, and NF-κB. ICI 118551 also reversed the effects of procaterol on cAMP levels. Procaterol may inhibit rhinovirus infection by reducing ICAM-1 and acidic endosomes as well as modulate airway inflammation in rhinovirus infection.Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
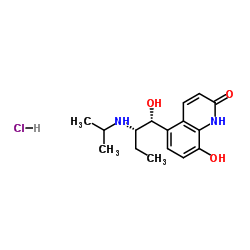 |
Procaterol Hydrochloride
CAS:62929-91-3 |
C16H23ClN2O3 |
|
Randomized, Multicenter Clinical Study of Tratinterol Hydroc...
2015-06-01 [Clin. Ther. 37 , 1248-58, (2015)] |
|
Adenosine activation of A(2B) receptor(s) is essential for s...
2011-08-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 301(2) , L171-80, (2011)] |
|
Aerosol characteristics of admixture of budesonide inhalatio...
2013-03-01 [Allergol. Int. 62(1) , 131-5, (2013)] |
|
Binding pockets of the beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenergic recep...
1999-11-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 56 , 875-885, (1999)] |
|
Metabolic response to various beta-adrenoceptor agonists in ...
1998-08-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 124 , 1684, (1998)] |