Antibody-conjugated soybean oil-filled calcium phosphate nanoshells for targetted delivery of hydrophobic molecules.
H T Schmidt, M Kroczynski, J Maddox, Y Chen, R Josephs, A E Ostafin
Index: J. Microencapsul. 23(7) , 769-81, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Hollow calcium phosphate nanoparticles capable of encapsulating poorly water-soluble molecules were produced by self-assembly. Previously reported were solid calcium phosphate nanoparticles and water-filled calcium phosphate nanocapsules suited for encapsulating mostly hydrophilic, but not hydrophobic compounds. Here, calcium phosphate was deposited around 100 nm diameter, 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate stabilized soybean oil nanoemulsions using either calcium chloride or NaOH titrations to achieve shell thickness between 20-70 nm. The surface was functionalized with carboxylic acid via the addition of carboxyethylphosphonic acid to attach Molecular Probes AB-594C antibody using sulpho-n-hydroxysuccinimide and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride with an efficiency of approximately 70%, while retaining near complete antibody function. Hydrophobic pyrene was encapsulated with an efficiency of 95%, at concentrations much higher than its water solubility limit, and exhibited spectral features characteristic of a hydrophobic environment. These materials can be used in the targeted delivery of many useful, yet poorly water-soluble pharmaceutical and nutraceutical compounds.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
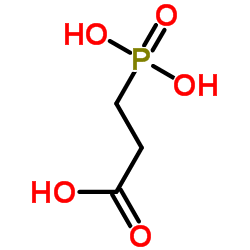 |
3-Phosphonopropanoic acid
CAS:5962-42-5 |
C3H7O5P |
|
Design of a metal primer containing a dithiooctanoate monome...
2011-01-01 [Dent. Mater. J. 30(3) , 300-7, (2011)] |
|
Effects of a newly designed HEMA-free, multi-purpose, single...
2011-01-01 [Dent. Mater. J. 30(5) , 616-25, (2011)] |
|
Cytocompatibility assessment of chemical surface treatments ...
2013-11-01 [J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 101(11) , 3301-10, (2013)] |
|
Inclusion of ionization states of ligands in affinity calcul...
2009-07-01 [Proteins 76(1) , 138-50, (2009)] |
|
Synthesis, chiral high performance liquid chromatographic re...
2010-05-13 [J. Med. Chem. 53(9) , 3454-64, (2010)] |