A novel role for histone methyltransferase KYP/SUVH4 in the control of Arabidopsis primary seed dormancy.
Jian Zheng, Fengying Chen, Zhi Wang, Hong Cao, Xiaoying Li, Xin Deng, Wim J J Soppe, Yong Li, Yongxiu Liu
Index: New Phytol. 193(3) , 605-16, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
• Seed dormancy controls germination and plays a crucial role in the life cycle of plants. Chromatin modifications are involved in the regulation of seed dormancy; however, little is known about the underlying mechanism. • KYP/SUVH4 is required for histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation. Mutations in this gene cause increased seed dormancy. KYP/SUVH4-overexpressing Arabidopsis plants show decreased dormancy. KYP/SUVH4 expression is regulated by abscisic acid (ABA) and gibberellins (GA). The sensitivity of seed germination to ABA and paclobutrazol (PAC) is enhanced slightly in kryptonite-2 (kyp-2) and suvh4-2/suvh5 mutants, but weakened in KYP/SUVH4-overexpressing plants. • In the kyp-2 mutant, several dormancy-related genes, including DOG1 and ABI3, show increased expression levels, in agreement with a negative role for KYP/SUVH4 in gene transcription. • Genetic analysis showed that DOG1 and HUB1 are epistatic to KYP/SUVH4, suggesting that these genes regulate seed dormancy in the same genetic pathway.© 2011 The Authors. New Phytologist © 2011 New Phytologist Trust.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
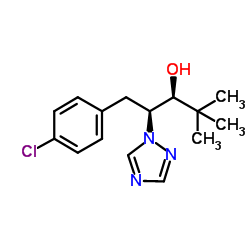 |
PACLOBUTRAZOL
CAS:76738-62-0 |
C15H20ClN3O |
|
ABA inhibits germination but not dormancy release in mature ...
2009-01-01 [J. Exp. Bot. 60 , 3387-96, (2009)] |
|
Dissipation and enantioselective degradation of plant growth...
2013-01-15 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(2) , 843-9, (2013)] |
|
The transcriptional regulator BBX24 impairs DELLA activity t...
2015-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 6 , 6202, (2015)] |
|
Azole drugs are imported by facilitated diffusion in Candida...
2010-01-01 [PLoS Pathog. 6 , e1001126, (2010)] |
|
Characterization of the procera tomato mutant shows novel fu...
2012-11-01 [Plant Physiol. 160(3) , 1581-96, (2012)] |