| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Manganese peroxidase from white-rot fungus (Phanerochaete chrysosporium)
CAS:114995-15-2 |
|
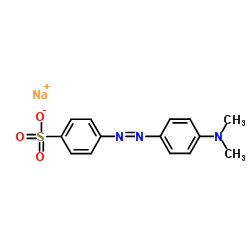 |
Methyl Orange
CAS:547-58-0 |