Swelling-shrinking behavior of chemically cross-linked polypeptide gels from poly(α-L-lysine), poly(α-DL-lysine), poly(ɛ-L-lysine) and thermally prepared poly(lysine): effects of pH, temperature and additives in the solution.
Mamoru K Kokufuta, Saigo Sato, Etsuo Kokufuta
Index: Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 87 , 299-309, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We synthesized the glutaraldehyde cross-linked hydrogels using four kinds of poly(lysine)s (PLs) and measured the equilibrium swelling ratio (Q) as a function of pH. Also measured was the temperature change of Q at a fixed pH (11.6) in the absence and presence of additives (LiBr, methanol and urea) that affect the secondary structure of PLs. The swelling data were examined using a force balance approach in which the repulsive and attractive interactions among the cross-linked PL chains were considered based on the conformational properties of PLs in aqueous solutions. It was found that the formation of the helical segments in the cross-linked chain has little effect in the gel collapse, but their association acts as the attractive interaction causing the gel to shrink. The formation of the beta-sheet structure within the network also acts as the attractive interaction. These attractive interactions are mainly due to the hydrogen bonding, but hydrophobic interactions between the lysine side chains should be considered. In addition, in the swelling behavior of all the PL gels the polyampholyte nature appears due to electrostatic interactions of the basic groups with the C-terminal carboxyl group.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
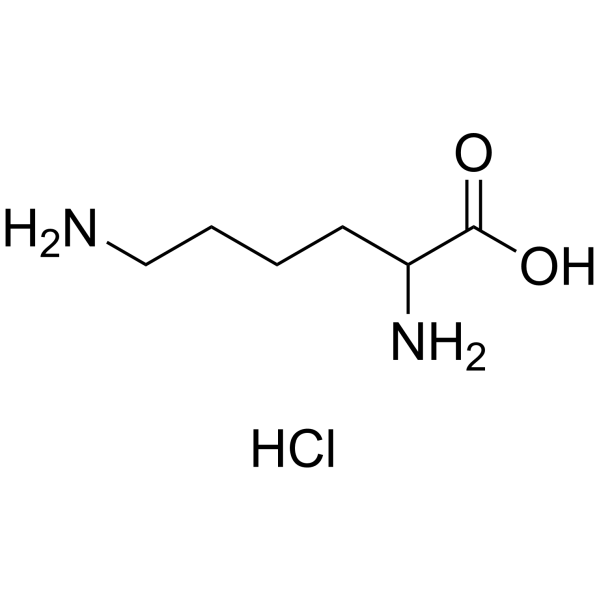 |
DL-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:70-53-1 |
C6H15ClN2O2 |
|
Influence of Free Amino Acids, Oligopeptides, and Polypeptid...
2015-06-10 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 5364-72, (2015)] |
|
Preparation of hierarchical mesocrystalline DL-lysine·HCl-po...
2011-08-16 [Adv. Mater. 23 , 3548-3552, (2011)] |
|
Reinvestigation on the buildup mechanism of alternate multil...
2008-12-02 [Langmuir 24 , 13426-13433, (2008)] |
|
Peptides with regular enantiomeric sequences: a wide class o...
2007-07-01 [J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 7 , 2230-2238, (2007)] |