Evidence for an involvement of NMDA and non-NMDA receptors in synaptic excitation of phrenic motoneurons in the rabbit.
G Böhmer, K Schmid, W Schauer
Index: Neurosci. Lett. 130(2) , 271-4, (1991)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The action of endogenous excitatory amino acids on phrenic motoneurons was studied in anesthetized, vagotomized, paralyzed and artificially ventilated rabbits. The NMDA receptor antagonists APV and ketamine, as well as the non-NMDA receptor antagonists GAMS and DNQX were administered by microinjection into the ventral horn of the spinal segments C3-C5. Injection of each antagonist resulted in a reversible reduction of the phrenic nerve activity. Results suggest an important function of endogenous excitatory amino acids in the excitation of phrenic motoneurons. NMDA as well as non-NMDA receptors are involved. The functional role of both receptor types in bulbospinal neurotransmission is discussed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
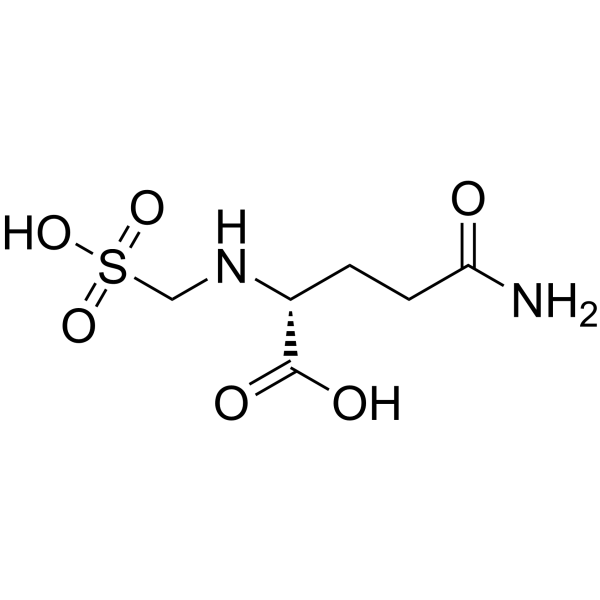 |
γ-D-Glutamylaminomethylsulfonic acid
CAS:90237-02-8 |
C6H12N2O6S |
|
Effects of some excitatory amino acid antagonists on imipene...
1995-02-06 [Brain Res. 671(1) , 131-40, (1995)] |
|
Glutamate and vasopressin interact to control scent marking ...
1996-08-26 [Brain Res. 731(1-2) , 213-6, (1996)] |
|
Excitatory neurotransmitters in the lateral habenula and ped...
1992-09-25 [Brain Res. 591(2) , 209-22, (1992)] |
|
Release of GABA from sensory neurons transduced with a GAD67...
2006-02-16 [Brain Res. 1073-1074 , 297-304, (2006)] |
|
Preferential block of desensitizing AMPA receptor in hippoca...
1995-09-15 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 284 , 141-147, (1995)] |