Cardiotoxicity of the lipophilic compound aluminum acetylacetonate in rabbits.
B Corain, P Zatta, G G Bombi, R Giordano
Index: Biomed. Environ. Sci. 1(3) , 283-7, (1988)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Aluminum acetylacetonate was administered to New Zealand white rabbits as liposome preparations and was found to distribute approximately 1:1 between water and phosphatidylcholine dipalmitoyl vesicles. Biochemical monitoring proved that after 2 weeks of daily injection of 40 micrograms of Al(III) in the above form, the animals developed significant signs of cardiac suffering, evidenced by variations in lactic dehydrogenase and creatinine phospokinase. Histopathologic investigation revealed that aluminum acetylacetonate caused unambiguous myocardial infarcts, characterized by myocardial contraction bands. In contrast, injection of Al(III) as a simple salt (lactate, 20 mg/day for 3 weeks) gave a less severe myocardiopathy, certainly not infarctual. Aluminum acetylacetonate given to rabbits appears to be, to our knowledge, the only chemical tool able to mimic spontaneous infarction situations in humans.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
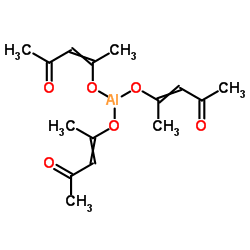 |
Aluminum acetylacetonate
CAS:13963-57-0 |
C15H21AlO6 |
|
Does aluminum lactate cause spinal cord infarction in rabbit...
1991-12-01 [Environ. Health Perspect. 96 , 245, (1991)] |
|
Low-temperature synthesis of gamma-alumina nanocrystals from...
2007-05-01 [Small 3(5) , 763-7, (2007)] |
|
Procedures for labeling the high-resolution axis of two-dime...
2002-01-01 [Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 21(1-2) , 21-43, (2002)] |
|
Experimental aluminum pathology in rabbits: effects of hydro...
1990-11-01 [Environ. Health Perspect. 89 , 217-23, (1990)] |
|
Effects of aluminum speciation on murine neuroblastoma cells...
1992-01-01 [Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 16(1-2) , 11-22, (1992)] |