| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
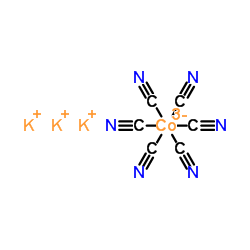 |
Potassium hexacyanocobaltate
CAS:13963-58-1 |
|
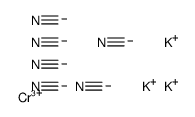 |
potassium chromic cyanide
CAS:13601-11-1 |