| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
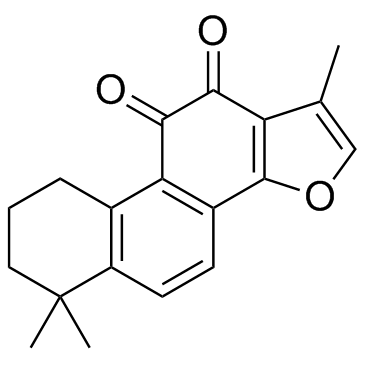 |
Tanshinone IIA
CAS:568-72-9 |
|
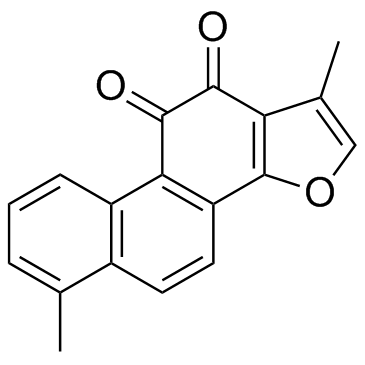 |
Tanshinone I
CAS:568-73-0 |
|
 |
Cryptotanshinone
CAS:35825-57-1 |