Determination of 4-methyl-cis-hexahydrophthalic anhydride in human blood by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection.
P Pfäffli, H Savolainen
Index: Analyst 116(12) , 1333-6, (1991)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A gas-chromatographic technique using 63Ni electron-capture detection was applied to the determination of 4-methyl-cis-hexahydrophthalic anhydride in the blood of workers occupationally exposed to this airborne agent. The detection limit was 0.24 nmol ml-1. For occupational exposure to between 0.14 and 0.31 mg m-3 of the anhydride, the anhydride concentration in the workers' blood samples ranged from 3.4 to 10.7 nmol ml-1. The results are consistent with earlier findings in animal exposure experiments and support the view that the hydrolysis of the anhydride in a biological medium is not spontaneous, but might be an enzyme-catalysed reaction. The resulting dicarboxylic acid is excreted by the kidneys without further conjugation reactions.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
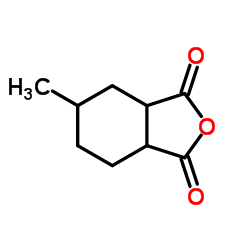 |
Hexahydro-4-methylphthalic anhydride
CAS:19438-60-9 |
C9H12O3 |
|
Delayed and immediate allergy caused by methylhexahydrophtha...
1997-01-01 [Contact Dermatitis 36(1) , 34-8, (1997)] |
|
Determination of hexahydrophthalic acid and methylhexahydrop...
1997-04-11 [J. Chromatogr. B. Biomed. Sci. Appl. 691(2) , 331-9, (1997)] |
|
Human hemoglobin adducts following exposure to hexahydrophth...
1998-12-01 [Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 153(2) , 152-60, (1998)] |
|
Mass spectrometric characterization of human hemoglobin addu...
2002-04-01 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 15(4) , 562-9, (2002)] |
|
Biological monitoring of methylhexahydrophthalic anhydride b...
1997-01-01 [Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 70(2) , 128-32, (1997)] |