| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
GERANYL PYROPHOSPHATE AMMONIUM 200
CAS:763-10-0 |
|
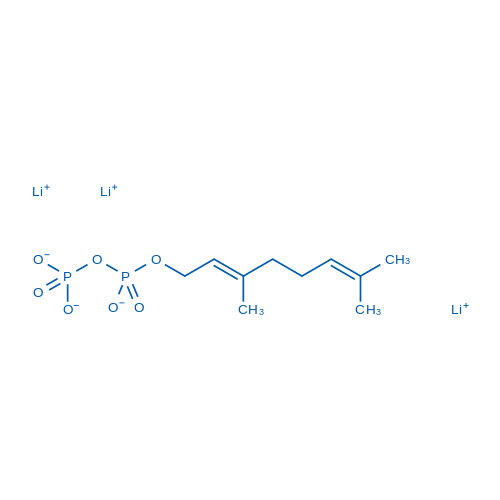 |
Geranyl pyrophosphate lithium salt
CAS:21141-43-5 |