| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
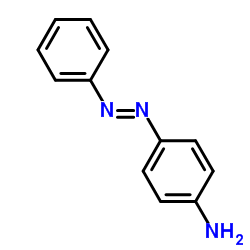 |
Aniline Yellow
CAS:60-09-3 |
|
 |
Epirizole
CAS:18694-40-1 |