Reduction of soybean meal non-starch polysaccharides and α-galactosides by solid-state fermentation using cellulolytic bacteria obtained from different environments.
Rafael Opazo, Felipe Ortúzar, Paola Navarrete, Romilio Espejo, Jaime Romero
Index: PLoS ONE 7(9) , e44783, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Soybean meal (SBM) is an important protein source in animal feed. However, the levels of SBM inclusion are restricted in some animal species by the presence of antinutritional factors (ANFs), including non-starch polysaccharides (NSPs) and α-galactosides (GOSs). The aim of this study was to reduce the soybean meal NSPs and GOSs by solid-state fermentation (SSF) using a combination of cellulolytic bacteria isolated from different environments (termites, earthworms, corn silage and bovine ruminal content). To analyse the key enzymatic activities, the isolates were grown in minimal media containing NSPs extracted from SBM. The selected bacterial strains belonged to the genera Streptomyces, Cohnella and Cellulosimicrobium. SSF resulted in a reduction of nearly 24% in the total NSPs, 83% of stachyose and 69% of raffinose and an increase in the protein content. These results suggest that cellulolytic bacteria-based SSF processing facilitates SBM nutritional improvement. In addition, the use of fermented SBM in animal diets can be recommended.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
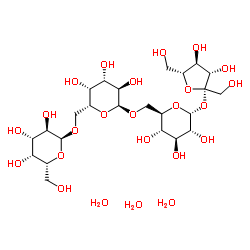 |
Lupeose
CAS:54261-98-2 |
C24H42O21 |
|
D-chiro-inositol affects accumulation of raffinose family ol...
2011-03-01 [J. Plant Physiol. 168(4) , 352-8, (2011)] |
|
Improved evaporative light scattering detection for carbohyd...
2015-08-01 [Food Chem. 180 , 265-71, (2015)] |
|
Functional analysis of family GH36 α-galactosidases from Rum...
2012-11-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78(21) , 7720-32, (2012)] |
|
Purification and characterization of Aspergillus terreus α-g...
2011-08-01 [Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 164(7) , 1111-25, (2011)] |
|
Nutritional potential of rice bean (Vigna umbellata): an und...
2013-01-01 [J. Food Sci. 78(1) , C8-16, (2013)] |