| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
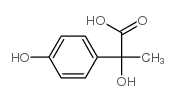 |
DL-p-Hydroxyphenyllactic acid
CAS:6482-98-0 |
|
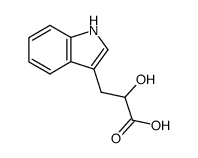 |
DL-INDOLE-3-LACTIC ACID
CAS:832-97-3 |