The effects of a cytokine suppressive anti-inflammatory drug on the output of prostaglandin E(2) and interleukin-1 beta from human fetal membranes.
M H F Sullivan, S A Alvi, N L Brown, M G Elder, P R Bennett
Index: Mol. Hum. Reprod. 8(3) , 281-5, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Fetal membranes are a primary source of prostaglandins and pro-inflammatory cytokines implicated in human parturition, so the inhibition of inflammatory pathways may be of benefit in pregnancies complicated by premature labour. We have therefore investigated the effects of a cytokine-suppressant anti-inflammatory drug (CSAID) on the output of prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and interleukin (IL)-1 beta from human fetal membranes in vitro. Bacterial endotoxin increased the expression of mRNA for IL-1 beta and type-2 cyclo-oxygenase (COX-2), and there were corresponding increases in the output of IL-1 beta protein and PGE(2). The CSAID decreased IL-1 beta protein, COX-2 expression and PGE(2) output, but not mRNA for IL-1 beta, indicating a post-translational effect on the production of IL-1 beta and a transcriptional affect on COX-2, with an overall reduction in PGE(2). These findings are consistent with the effects of CSAIDs in other systems, and indicate that they are of possible use in premature labour.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
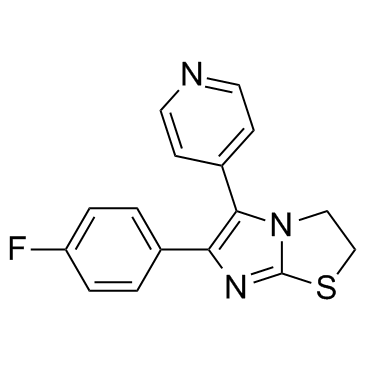 |
SKF 86002
CAS:72873-74-6 |
C16H12FN3S |
|
The discovery of novel chemotypes of p38 kinase inhibitors.
2005-01-01 [Curr. Top. Med. Chem 5(10) , 953-65, (2005)] |
|
Activation of p38MAPK contributes to expanded polyglutamine-...
2008-01-01 [PLoS ONE 3(5) , e2130, (2008)] |
|
Differential activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathw...
2002-07-01 [Toxicol. Sci. 68(1) , 82-92, (2002)] |
|
A Biacore biosensor method for detailed kinetic binding anal...
2004-02-01 [Anal. Biochem. 325(1) , 126-36, (2004)] |
|
Lipopolysaccharide: a p38 MAPK-dependent disrupter of neutro...
2005-01-01 [Microcirculation 12(5) , 421-32, (2005)] |