| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
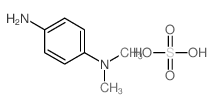 |
N,N-Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine sulfate salt
CAS:536-47-0 |
|
 |
p-Dimethylaminoaniline dihydrochloride
CAS:536-46-9 |
|
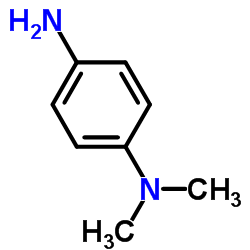 |
N,N-Dimethyl-1,4-benzenediamine
CAS:99-98-9 |
|
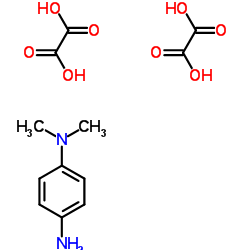 |
N,N-Dimethyl-1,4-phenylenediamine oxalate
CAS:62778-12-5 |