Probing key targets in insulin signaling and adipogenesis using a methanolic extract of Costus pictus and its bioactive molecule, methyl tetracosanoate.
Kusampudi Shilpa, Kadapakkam Nandabalan Sangeetha, Velusamy Shanmuganathan Muthusamy, Sundaresan Sujatha, Baddireddi Subadhra Lakshmi
Index: Biotechnol. Lett. 31(12) , 1837-41, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A methanolic extract of Costus pictus (CPME) showed optimum anti-diabetic activity at 100 ng/ml. Bioactivity-guided purification of CPME led to the isolation of methyl tetracosanoate (MT) which showed an optimum glucose uptake at 1 ng/ml. CPME at 10 mug/ml inhibited adipogenesis whereas fully differentiated adipocytes exhibited a 3-fold increase in lipid accumulation compared to pre-adipocytes. Gene and protein expression of key targets in insulin signaling and adipogenesis pathway revealed that CPME exhibited anti-diabetic activity along with anti-adipogenic activity whereas MT demonstrated only anti-diabetic activity.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
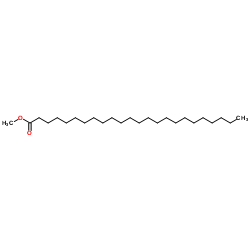 |
Methyl Lignocerate
CAS:2442-49-1 |
C25H50O2 |
|
In-house validation of an improved sample extraction and cle...
2003-06-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 376 , 360-365, (2003)] |
|
Diagnostic patterns of very-long-chain fatty acids in plasma...
2001-08-25 [J. Chromatogr. B. Biomed. Sci. Appl. 760 , 149-157, (2001)] |
|
Analysis of mycolic acid cleavage products and cellular fatt...
1986-04-01 [J. Clin. Microbiol. 23(4) , 731-6, (1986)] |
|
Rapeseed oil methyl ester pyrolysis: on-line product analysi...
2011-05-27 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1218 , 3217-3223, (2011)] |
|
Sequential pressurized liquid extraction to determine brain-...
2006-09-15 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1127 , 26-33, (2006)] |