[Occupational hygiene in production and use of multicomponent metal compounds].
A I Fadeev
Index: Med. Tr. Prom. Ekol. (10) , 4-6, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The article deals with results obtained in hygienic evaluation of production and application of new monocrystalline compounds based on cesium, sodium, iodine, lead, scandium, fluorine. The evaluation covered work conditions and health state of those engaged into production of monocrystalline compounds, revealed the main occupational hazards. The experiments determined fundamental toxicometric parameters, studied characteristics of general toxic and specific effects induced by lead fluoride and cesium iodine. The results formed basis for sanitary measures, establishment of MACs for 4 monocrystalline compounds in the air of workplace.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
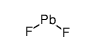 |
Lead fluoride
CAS:7783-46-2 |
F2Pb |
|
Enhancement of luminescence properties in Er3+ doped TeO2-Na...
2007-04-01 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 66(4-5) , 1052-7, (2007)] |
|
EPR and optical studies of erbium-doped beta-PbF2 single-cry...
2007-11-07 [Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9(41) , 5591-8, (2007)] |
|
[The late effects of exposure to lead fluoride].
1992-03-01 [Gig. Sanit. (3) , 28-9, (1992)] |
|
Anion exchange of the cationic layered material [Pb2F2]2+.
2012-07-04 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(26) , 10729-32, (2012)] |
|
PbF2 compared to Al2O3 and AlF3 to produce an epithermal neu...
1996-02-01 [Med. Phys. 23(2) , 279-80, (1996)] |