Chemosensitization of fungal pathogens to antimicrobial agents using benzo analogs.
Jong H Kim, Noreen Mahoney, Kathleen L Chan, Russell J Molyneux, Gregory S May, Bruce C Campbell
Index: FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 281(1) , 64-72, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Activities of conventional antifungal agents, fludioxonil, strobilurin and antimycin A, which target the oxidative and osmotic stress response systems, were elevated by coapplication of certain benzo analogs (aldehydes and acids). Fungal tolerance to 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde or 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid was found to rely upon mitochondrial superoxide dismutase (SOD2) or glutathione reductase (GLR1), genes regulated by the HOG1 signaling pathway, respectively. Thus, certain benzo analogs can be effective at targeting cellular oxidative stress response systems. The ability of these compounds to chemosensitize fungi for improved control with conventional antifungal agents is discussed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
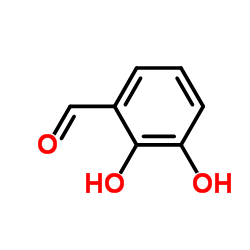 |
2,3-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde
CAS:24677-78-9 |
C7H6O3 |
|
Self-activating nuclease activity of copper (II) complexes o...
2006-01-01 [J. Inorg. Biochem. 100(1) , 51-7, (2006)] |
|
Synthesis and biological activity of 4-amino-5-chloro-2-etho...
1996-08-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 44(8) , 1484-92, (1996)] |
|
Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol kinase by toyocamycin.
1990-12-01 [J. Antibiot. 43 , 1586-1589, (1990)] |
|
Effective photocatalytic dechlorination of 2,4-dichloropheno...
2016-01-01 [Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 15 , 86-98, (2016)] |
|
[Studies on chemical constituents from Elaeocarpus sylvestri...
2008-10-01 [Zhong Yao Cai 31(10) , 1503-5, (2008)] |