An effective use of benzoic anhydride and its derivatives for the synthesis of carboxylic esters and lactones: a powerful and convenient mixed anhydride method promoted by basic catalysts.
Isamu Shiina, Mari Kubota, Hiromi Oshiumi, Minako Hashizume
Index: J. Org. Chem. 69(6) , 1822-30, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Various carboxylic esters are obtained at room temperature in excellent yields with high chemoselectivities from nearly equimolar amounts of carboxylic acids and alcohols using 2-methyl-6-nitrobenzoic anhydride with triethylamine by the promotion of a basic catalyst such as 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine. A variety of lactones are also prepared in high yields at room temperature from the corresponding omega-hydroxycarboxylic acids with use of 2-methyl-6-nitrobenzoic anhydride in the presence of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine. A similar reaction occurs with triethylamine when using a catalytic amount of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine 1-oxide as an effective promoter for the intramolecular condensation reaction. These methods are successfully applied to the synthesis of erythro-aleuritic acid lactone and an eight-membered-ring lactone moiety of octalactins A and B. The efficiency of the cyclizations is compared to those of other reported lactonizations.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
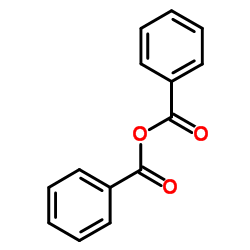 |
Benzoic anhydride
CAS:93-97-0 |
C14H10O3 |
|
Regioselective benzoylation of glycopyranosides by benzoic a...
2012-10-01 [Carbohydr. Res. 359 , 111-9, (2012)] |
|
Introduction of a benzoyl group onto 6-chloropurine riboside...
2000-01-01 [Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 44 , 103-104, (2000)] |
|
Derivatization for LC-electrospray ionization-MS: a tool for...
2004-05-15 [Anal. Chem. 76(10) , 2869-77, (2004)] |
|
Ru(II) multinuclear metallosupramolecular rack-type architec...
2010-05-17 [Chemistry 16(19) , 5645-60, (2010)] |
|
Benzoolysis of diacylglycerophosphocholines: dephosphorylati...
1996-06-01 [J. Lipid Res. 37(6) , 1224-33, (1996)] |