Multifunctional action of antifungal polygodial against Saccharomyces cerevisiae: involvement of pyrrole formation on cell surface in antifungal action.
Ken-ichi Fujita, Isao Kubo
Index: Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13(24) , 6742-7, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The antifungal activity of polygodial against Saccharomyces cerevisiae involves multifunctions. Polygodial first acts as a surface-active agent (surfactant) and then becomes involved in biochemical processes. The ability to form a pyrrole derivative with a primary amine group of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and phosphatidylserine (PS) in the outer monolayer of the plasma membrane is likely, in part, an initial step in the antifungal action of polygodial. In the lipid fraction derived from cells treated with polygodial, no PE and PS were detected, indicating a disturbance in the balance of the plasma membrane. The primary antifungal action of polygodial comes from its ability to act as a surfactant that nonspecifically disrupts the lipid-protein interface of integral proteins, denaturing their functioned conformation. Once polygodial enters the cytoplasm by destroying the membrane barrier, it reacts with L-cystein-containing cytoplasmic materials, such as a small molecule, glutathione, and a protein, alcohol dehydrogenase, to potentiate the antifungal action.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
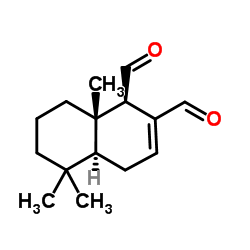 |
(-)-Polygodial
CAS:6754-20-7 |
C15H22O2 |
|
Screening for negative effects of candidate ascidian antifou...
2013-01-01 [Biofouling 29(1) , 29-37, (2013)] |
|
Preventing ascidian fouling in aquaculture: screening select...
2012-01-01 [Biofouling 28(1) , 39-49, (2012)] |
|
Inhibition of the mitochondrial ATP synthesis by polygodial,...
2005-07-01 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 70(1) , 82-9, (2005)] |
|
Antibacterial activity of polygodial.
2005-12-01 [Phytother Res. 19(12) , 1013-7, (2005)] |
|
Synergism of polygodial and trans-cinnamic acid on inhibitio...
2003-10-01 [J. Chem. Ecol. 29(10) , 2253-62, (2003)] |