An attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR FT-IR) spectroscopic study of gas adsorption on colloidal stearate-capped ZnO catalyst substrate.
Ian P Silverwood, Colin W Keyworth, Neil J Brown, Milo S P Shaffer, Charlotte K Williams, Klaus Hellgardt, Geoff H Kelsall, Sergei G Kazarian
Index: Appl. Spectrosc. 68(1) , 88-94, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR FT-IR) spectroscopy has been applied in situ to study gas adsorption on a colloidal stearate-capped zinc oxide (ZnO) surface. Infrared spectra of a colloidal stearate-capped ZnO catalyst substrate were assigned at room temperature using zinc stearate as a reference compound. Heating was shown to create a monodentate species that allowed conformational change to occur, leading to altered binding geometry of the stearate ligands upon cooling. CO2 and H2 adsorption measurements demonstrated that the ligand shell was permeable and did not cover the entire surface, allowing adsorption and reaction with at least some portion of the ZnO surface. It has been demonstrated that stearate ligands did not prevent the usual chemisorption processes involved in catalytic reactions on a model ZnO catalyst system, yet the ligand-support system is dynamic under representative reaction conditions.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
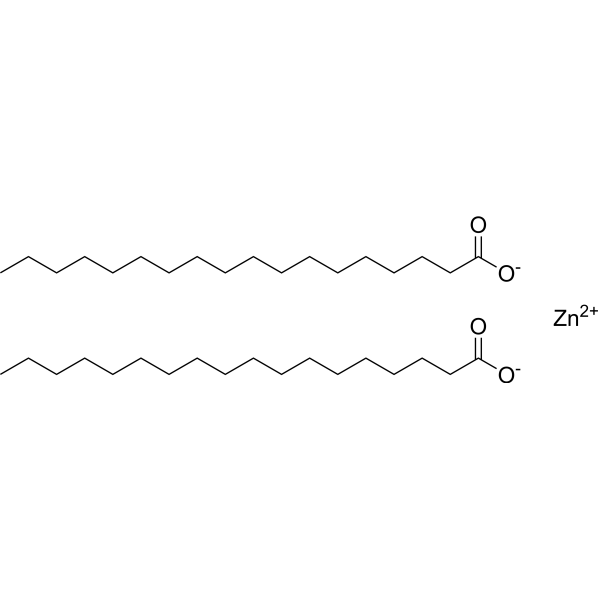 |
Zinc stearate
CAS:557-05-1 |
C36H70O4Zn |
|
Low-temperature processed Ga-doped ZnO coatings from colloid...
2013-03-06 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135(9) , 3439-48, (2013)] |
|
Possibility of alveolar bone promoting enhancement by using ...
2012-01-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 35(9) , 1496-501, (2012)] |
|
Effect of zinc stearate and/or epoxidized soybean oil on gel...
[J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 74(10) , 2488-98, (1999)] |
|
Ionic thermoplastic elastomer based on maleated EPDM rubber....
[J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 61(1) , 177-86, (1996)] |
|
The effect of zinc stearate on melt-processable ionomeric bl...
[Polymer 40(6) , 1487-93, (1999)] |