Prognostic value of anterior rhinomanometry in diode laser turbinoplasty.
Gerd Fabian Volk, Mira Pantel, Orlando Guntinas-Lichius, Claus Wittekindt
Index: Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 136(10) , 1015-9, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To identify objective criteria predicting the success of diode laser-assisted turbinoplasty.Prospective before-and-after trial with follow-up of 8 weeks.Outpatient department of a tertiary referral center.Forty-one patients with nasal obstruction caused by hyperplastic inferior nasal turbinates.Active anterior rhinomanometry with and without decongestion was used to assess the patients both before and after diode laser-assisted turbinate surgery. Surgery was performed under local anesthesia in "contact mode" using a continuous diode laser. In addition, a questionnaire assessed the subjective postoperative benefit.Presurgical effect of topical decongestion was correlated with postoperative improvement of nasal airflow and patients' subjective satisfaction.Turbinoplasty significantly improved the mean (SD) nasal airflow by 37.1% (52.4%) (95% confidence interval [CI], 20.6%-53.7%), from 509.8 (189.2) cm³/s (95% CI, 450.1-569.5) to 660.9 (285.4) cm³/s (95% CI, 570.8-751.0) (P < .001). There was no significant correlation between patients' subjective satisfaction and improvement of nasal airflow postoperatively (r(s) = -0.01; P = .93). There was a strong correlation between the presurgical effect of topical decongestion and the improvement of nasal airflow by surgery (r(s) = 0.42; P = .01). The correlation was even stronger when the absolute values were adjusted by the preoperative nasal airflow baseline (r(s) = 0.55; P = .01).Rhinomanometry with topical decongestion has a high predictive value for the objective outcome of diode laser-assisted turbinoplasty. Thus, performing a rhinomanometry with topical decongestion and calculating the relative spread of decongestion can help to estimate the patients' benefit from diode laser-assisted turbinate surgery.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
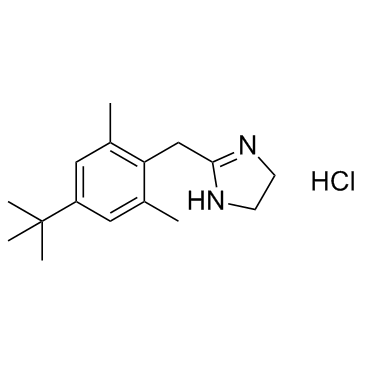 |
Xylometazoline hydrochloride
CAS:1218-35-5 |
C16H25ClN2 |
|
[Nasal decongestants and eye drops: keep out of children's r...
2013-01-01 [Perspect. Infirm. 10(2) , 63, (2013)] |
|
Intranasal topical local anesthetic and decongestant for fle...
2013-12-01 [JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 139(12) , 1301-5, (2013)] |
|
Xylometazoline pretreatment reduces nasotracheal intubation-...
2010-10-01 [Br. J. Anaesth. 105(4) , 501-5, (2010)] |
|
Preparation of nose for nasal endoscopy: cotton pledget pack...
2013-01-01 [Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 270(1) , 117-21, (2013)] |
|
Nasal inspiratory flow: at rest and sniffing.
2011-01-01 [Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 1(2) , 128-35, (2011)] |