| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
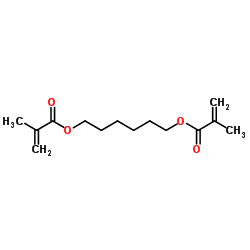 |
1,6-Hexanediyl bis(2-methylacrylate)
CAS:6606-59-3 |
|
 |
Poly(ethyl methacrylate)
CAS:9003-42-3 |