Is homatropine 5% effective in reducing pain associated with corneal abrasion when compared with placebo? A randomized controlled trial.
Robert Meek, Andy Sullivan, Marcel Favilla, Ian Larmour, Steven Guastalegname
Index: Emerg. Med. Australas. 22(6) , 507-13, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To compare the change in visual analogue scale (VAS) pain ratings over 24 h following mechanical corneal abrasion between patients receiving sixth hourly drops of either 5% homatropine or placebo.A triple blind randomized controlled trial was conducted on a convenience sample of eligible consenting adults who were randomized to receive either sixth hourly 5% homatropine (active) or 0.5% hypromellose (placebo) eye drops. VAS pain ratings were performed at 0, 6, 12, 18 and 24 h whereas the study drug was instilled at 0, 6, 12 and 18 h. The primary outcome was attainment of a clinically significant reduction in pain on the VAS (>20 mm decrease) from enrolment to each time point.There were no significant differences in baseline variables or VAS pain ratings at any time point between those in the homatropine (n= 20) and placebo (n= 20) groups. The percentages of patients reporting a >20 mm VAS decrease at 12 h were 50% (95% CI -27.2-72.8) and 60% (95% CI -36.1-80.9) for the homatropine and placebo groups, respectively.We found no significant difference in pain score reductions between the two groups but some level of therapeutic benefit is not excluded.© 2010 The Authors. EMA © 2010 Australasian College for Emergency Medicine and Australasian Society for Emergency Medicine.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
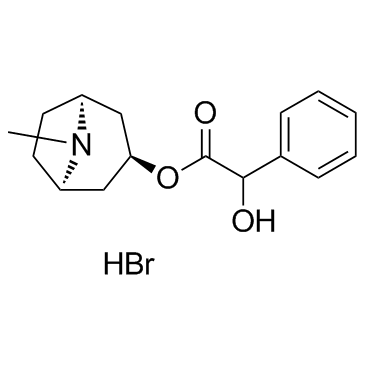 |
Homatropine (Bromide)
CAS:51-56-9 |
C16H22BrNO3 |
|
The endogenous cannabinoid, anandamide, inhibits dopamine tr...
2010-03-01 [J. Neurochem. 112(6) , 1454-64, (2010)] |
|
Efficacy of tropicamide, homatropine, cyclopentolate, atropi...
2011-11-01 [N. Z. Vet. J. 59(6) , 328-31, (2011)] |
|
Dense membrane formation after combined phacoemulsification-...
2005-06-01 [Clin. Experiment. Ophthalmol. 33(3) , 296-7, (2005)] |
|
Hypotony maculopathy in a patient with HLA-B27-associated uv...
2008-01-01 [Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 16(3) , 107-8, (2008)] |
|
Bilateral microbial keratitis in highly active antiretrovira...
2011-10-01 [Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 19(5) , 343-5, (2011)] |