Sage weed (Salvia plebeia) extract antagonizes foam cell formation and promotes cholesterol efflux in murine macrophages.
Sin-Hye Park, Jung-Lye Kim, Min-Kyung Kang, Ju-Hyun Gong, Seon-Young Han, Jae-Hoon Shim, Soon Sung Lim, Young-Hee Kang
Index: Int. J. Mol. Med. 30(5) , 1105-12, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Lipid-laden peripheral tissue cells release cholesterol to an extracellular acceptor such as high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Foam cells are formed at the first stage of atherosclerosis development. This study investigated whether sage weed (Salvia plebeia) extract (SWE) influences cholesterol handling of J774A1 murine macrophages. A murine macrophage cell line, J774A1, was used in this study. Oxidized low-density lipoproteins (LDL) treatment was used for foam cell formation, which was confirmed using Oil red O staining. The oxidized LDL uptake and cholesterol efflux from lipid-laden foam cell-associated proteins were detected by western blot analysis. Also, transcriptional levels of these associated genes were examined using reverse transcription-PCR. Also, cholesterol efflux was measured using NBD-cholesterol efflux assay. Non-toxic SWE at ≥10 µg/ml attenuated scavenger receptor (SR)-B1 expression of macrophages induced by oxidized LDL for 6 h, which was achieved at its transcriptional levels. Consistently, SWE suppressed oxidized LDL-stimulated cellular lipid accumulation and foam cell formation due to downregulated SR-B1. SWE upregulated the protein expression and mRNA levels of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 (ABCG1) in lipid-laden foam cells, both responsible for cholesterol efflux. In addition, SWE promoted apolipoprotein E (apoE) secretion from oxidized LDL-induced foam cells. Cholesterol efflux was enhanced by ≥10 µg/ml SWE most likely through the induction of ABCA1 and ABCG1 and the secretion of apoE. Although 10 µM homoplantaginin, a compound mainly present in sage weeds, did not influence cellular expression of ABCA1 and ABCG1, it suppressed oxidized LDL-enhanced SR-B1 induction and foam cell formation. These results demonstrate that SWE antagonized oxidized LDL uptake and promoted cholesterol efflux in lipid-laden macrophages. Therefore, SWE may serve as a protective therapeutic agent against the development of atherosclerosis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
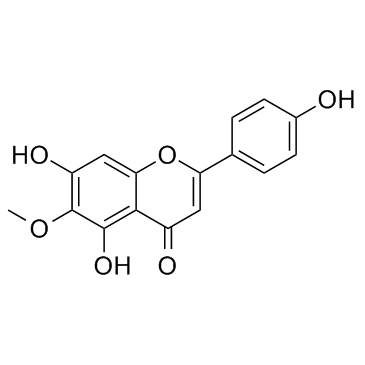 |
Hispidulin
CAS:1447-88-7 |
C16H12O6 |
|
Analysis of vervain flavonoids by HPLC/Diode array detector ...
1999-11-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 47(11) , 4579-82, (1999)] |
|
Inhibition of [methyl-3H]diazepam binding to rat brain membr...
1994-09-01 [Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 15(5) , 385-8, (1994)] |
|
Chemical fingerprint and quantitative analysis of Salvia ple...
2008-09-10 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 48(1) , 100-4, (2008)] |
|
Hispidulin protection against hepatotoxicity induced by brom...
1994-01-01 [Life Sci. 55(8) , PL145-50, (1994)] |
|
Hispidulin attenuates bone resorption and osteoclastogenesis...
2013-09-05 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 715(1-3) , 96-104, (2013)] |