| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
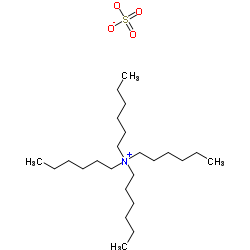 |
tetrahexylammonium sulfate
CAS:32503-34-7 |
|
 |
N,N,N-Trihexyl-1-hexanaminium bromide
CAS:4328-13-6 |