The effect of intestinal microflora on the enterohepatic circulation of mercapturic acid pathway metabolites.
J A Gustafsson, J J Rafter, J E Bakke, B E Gustafsson
Index: Nutr. Cancer 2(4) , 224-31, (1981)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The metabolism of four xenobiotics, pentachloromethylthiobenzene, 2-chloro-n-iso-propylacetanilide, 2-acetamido-4-(chloromethyl) thiazole and 2,4',5-trichlorobiphenyl, which are known to be metabolized via the mercapturic acid pathway, was examined in germfree and conventional rats. An essential role for the intestinal flora in the metabolism of the above compounds and in the production of certain metabolites was established. Mechanisms for the formation of these latter metabolites from the mercapturates are proposed. These mechanisms involve enterohepatic circulation and metabolism by the intestinal flora. The significance of xenobiotic metabolism by the intestinal microflora is discussed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
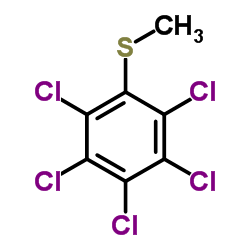 |
pentachloromethylthiobenzene
CAS:1825-19-0 |
C7H3Cl5S |
|
Comparison of bifunctional chelates for (64)Cu antibody imag...
2010-11-01 [Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 37(11) , 2117-26, (2010)] |
|
(68)Ga small peptide imaging: comparison of NOTA and PCTA.
2012-11-21 [Bioconjug. Chem. 23(11) , 2239-46, (2012)] |
|
The metabolism of pentachloromethylthiobenzene in germ-free ...
1981-03-01 [Xenobiotica 11(3) , 173-8, (1981)] |
|
Hexachlorobenzene (HCB) and some of its sulfur-containing me...
1980-01-01 [Dev. Toxicol. Environ. Sci. 8 , 627-30, (1980)] |
|
Effects of sulfur-containing metabolites of hexachlorobenzen...
1990-05-01 [J. Pharmacobiodyn. 13(5) , 278-84, (1990)] |