Characterization of the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of doxycycline and minocycline in different experimental models.
Leandro Francisco S Bastos, Leonardo A Merlo, Leonardo Tadeu S Rocha, Márcio M Coelho
Index: Eur. J. Pharmacol. 576(1-3) , 171-9, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Tetracyclines induce anti-inflammatory effects unrelated to their antimicrobial activities. We investigated the effect induced by minocycline and doxycycline in models of nociceptive and inflammatory pain, edema, fever, cell migration and formation of fibrovascular tissue, as these effects have not been fully investigated. Tetracyclines were administered via intraperitoneal route 1 h before the tests. Minocycline and doxycycline (100 mg/kg) inhibited the second phase of the formalin-induced nociceptive response in mice. Doxycycline (100 mg/kg) also inhibited the first phase. The nociceptive response induced by phorbol 12,13-didecanoate (PDD) in mice was inhibited by doxycycline (100 mg/kg). Furthermore, carrageenan-induced mechanical allodynia in rats was inhibited by doxycycline and minocycline (50 or 100 mg/kg). However, they did not enhance the latency in the hot-plate test. It is unlikely that antinociception resulted from motor incoordination or muscle relaxing effect, as both tetracyclines (100 mg/kg) did not impair the motor activity of mice in the rota-rod test. Doxycycline (50 or 100 mg/kg) or minocycline (50 or 100 mg/kg) inhibited carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats. However, only minocycline (100 mg/kg) inhibited PDD-induced edema. Carrageenan-induced leukocyte migration into the peritoneal cavity of rats was inhibited by both tetracyclines (100 mg/kg). Endotoxin-induced fever in rats was also inhibited by doxycycline (50 or 100 mg/kg) or minocycline (100 mg/kg). Finally, formation of fibrovascular tissue induced by subcutaneous implant of a cotton pellet in mice was inhibited by a 6-day administration of both tetracyclines (50 or 100 mg/kg day). Concluding, this study clearly shows the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of these second-generation tetracyclines.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
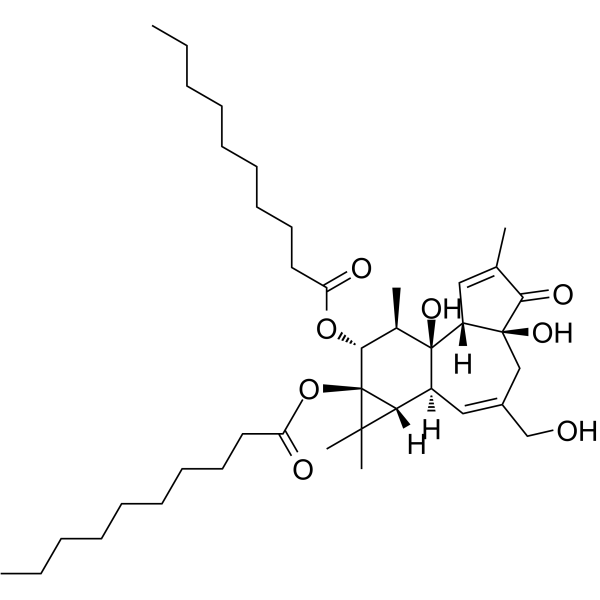 |
4alpha-PDD
CAS:27536-56-7 |
C40H64O8 |
|
Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPV4 channels in migration of rat ...
2012-09-01 [Pflugers Arch. 464(3) , 261-72, (2012)] |
|
Ca2+ entry via alpha1G and TRPV4 channels differentially reg...
2009-10-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 297(4) , L650-7, (2009)] |
|
Salt intake augments hypotensive effects of transient recept...
2009-02-01 [Hypertension 53(2) , 228-35, (2009)] |
|
Axonal neuropathy-associated TRPV4 regulates neurotrophic fa...
2012-02-17 [J. Biol. Chem. 287(8) , 6014-24, (2012)] |
|
Phosphorylation on the Ser 824 residue of TRPV4 prefers to b...
2012-03-01 [Cell. Signal. 24(3) , 641-51, (2012)] |