| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
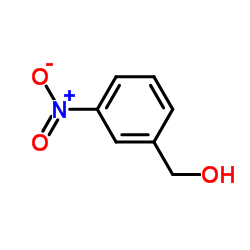 |
3-Nitrobenzenemethanol
CAS:619-25-0 |
|
 |
trisodium phosphate
CAS:7601-54-9 |
|
 |
3,4-Dihydro-2H-pyran
CAS:110-87-2 |