Separative recovery with lime of phosphate and fluoride from an acidic effluent containing H3PO4, HF and/or H2SiF6.
Mbarka Gouider, Mongi Feki, Sami Sayadi
Index: J. Hazard. Mater. 170(2-3) , 962-8, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Fluoride content and flow-rate of fertilizer plant wastewater from phosphoric acid and/or triple superphosphate (TSP) production lead to the discharge of several thousand tons of fluoride (F(-)) per year and even more for phosphate (PO4(3-)). Since sustainability is an important environmental concern, the removal methods should allow phosphorus and fluoride to be recycled as a sustainable products for use as raw materials either in agricultural or industrial applications. In the present work, separative recovery with lime of these two target species was investigated. A preliminary speciation study, carried out on the crude effluent, showed that two forms of fluoride: HF and H2SiF6 are present in a highly acidic medium (pH approximately 2). Evidence that fluoride is present under both free (HF) and combined (H2SiF6) forms, in the phosphate-containing effluent, was provided by comparing potentiometric titration curves of a crude wastewater sample and synthetic acid mixtures containing H3PO4, HF and H2SiF6. In a second step synthetic effluent containing mixtures of the following acids: HF, H2SiF6 and H3PO4, were treated with lime. The behaviour of these compounds under lime treatment was analysed. The data showed that fluoride has a beneficial effect on phosphate removal. Moreover, by acting on the precipitation pH, a "selective" recovery of fluoride and phosphate ions was possible either from phosphoric acid/hydrofluoric acid or phosphoric acid/hexafluorosilicic acid mixtures. Indeed, the first stage of the separative recovery, led to a fluoride removal efficiency of 97-98% from phosphoric acid/hydrofluoric acid mixture. It was of 93-95% from phosphoric acid/hexafluorosilicic acid mixture. During the second stage, the phosphate precipitation reached 99.8% from both acidic mixtures whereas it did not exceed 82% from a solution containing H3PO4 alone. The XRD and IR analyses showed that during lime treatment, a H2SiF6 hydrolysis occurred, instead of CaSiF6 solid formation, leading to CaF2 precipitate. Calcium fluoride and calcium phosphate based-by-products resulting from the two-step treatment process can be used as raw materials in several industrial sectors, such as ceramic and phosphate fertilizer industries.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
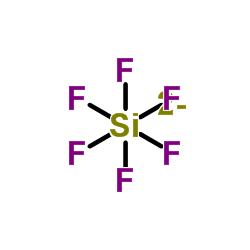 |
Hexafluorosilicate
CAS:16961-83-4 |
H2SiF6 |
|
Effects of ammonium hexafluorosilicate concentration on dent...
2010-01-01 [Dent. Mater. 26(1) , 29-34, (2010)] |
|
Microtensile bond strength of two single-step adhesive syste...
2001-07-01 [J. Adhes. Dent. 3(2) , 129-36, (2001)] |
|
Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction is not potentiated by rep...
1985-12-01 [Anesthesiology 63(6) , 608-10, (1985)] |
|
Community health effects of a municipal water supply hyperfl...
1988-06-01 [Am. J. Public Health 78(6) , 711-3, (1988)] |
|
Recovery of high surface area mesoporous silica from waste h...
2010-01-15 [J. Hazard. Mater. 173(1-3) , 576-80, (2010)] |