ATF6beta is a host cellular target of the Toxoplasma gondii virulence factor ROP18.
Masahiro Yamamoto, Ji Su Ma, Christina Mueller, Naganori Kamiyama, Hiroyuki Saiga, Emi Kubo, Taishi Kimura, Toru Okamoto, Megumi Okuyama, Hisako Kayama, Kisaburo Nagamune, Seiji Takashima, Yoshiharu Matsuura, Dominique Soldati-Favre, Kiyoshi Takeda
Index: J. Exp. Med. 208 , 1533-46, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The ROP18 kinase has been identified as a key virulence determinant conferring a high mortality phenotype characteristic of type I Toxoplasma gondii strains. This major effector molecule is secreted by the rhoptries into the host cells during invasion; however, the molecular mechanisms by which this kinase exerts its pathogenic action remain poorly understood. In this study, we show that ROP18 targets the host endoplasmic reticulum-bound transcription factor ATF6β. Disruption of the ROP18 gene severely impairs acute toxoplasmosis by the type I RH strain. Because another virulence factor ROP16 kinase modulates immune responses through its N-terminal portion, we focus on the role of the N terminus of ROP18 in the subversion of host cellular functions. The N-terminal extension of ROP18 contributes to ATF6β-dependent pathogenicity by interacting with ATF6β and destabilizing it. The kinase activity of ROP18 is essential for proteasome-dependent degradation of ATF6β and for parasite virulence. Consistent with a key role for ATF6β in resistance against this intracellular pathogen, ATF6β-deficient mice exhibit a high susceptibility to infection by ROP18-deficient parasites. The results reveal that interference with ATF6β-dependent immune responses is a novel pathogenic mechanism induced by ROP18.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
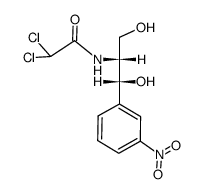 |
m-Chloramphenicol
CAS:7411-65-6 |
C11H12Cl2N2O5 |
|
Influence of dTMP on the phenotypic appearance and intracell...
2008-04-01 [Infect. Immun. 76(4) , 1333-9, (2008)] |
|
The transforming parasite Theileria co-opts host cell mitoti...
2010-01-01 [PLoS Biol. 8 , (2010)] |
|
Airtight storage of moist wheat grain improves bioethanol yi...
2009-01-01 [Biotechnol. Biofuels 2(1) , 16, (2009)] |
|
Distinctive contributions of the ribosomal P-site elements m...
2013-05-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 41 , 4963-75, (2013)] |