| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
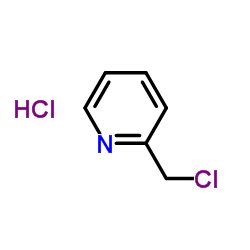 |
2-(Chloromethyl)pyridine HCl
CAS:6959-47-3 |
|
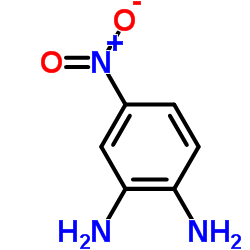 |
1,2-Diamino-4-nitrobenzene
CAS:99-56-9 |