Biological monitoring of dinitrotoluene by gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of 2,4-dinitrobenzoic acid in human urine.
J Angerer, A Weismantel
Index: J. Chromatogr. B. Biomed. Sci. Appl. 713(2) , 313-22, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The method of analysis described permits the determination of 2,4-dinitrobenzoic acid down to the lower microg l(-1) range in the urine of persons exposed to dinitrotoluene. 2,4-Dinitrobenzoic acid is the main metabolite of 2,4-dinitrotoluene and technical dinitrotoluene. After acidic hydrolysis, which served to release the conjugated part of the 2,4-dinitrobenzoic acid, the analyte was selectively separated from the urine matrix via various extraction steps and then derivatised to the methyl ester. Quantitative analysis was carried out using capillary gas chromatography and mass selective detection. 3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid was used as an internal standard. The detection limit was 1 microg l(-1) urine. The relative standard deviations of within-series imprecision were between 5 and 6%. The relative recoveries were between 91 and 110% depending on the concentration. The analytical method developed as part of this study was used to investigate a collective consisting of 82 urine samples from persons working in the area of explosives disposal. The concentrations of 2,4-dinitrobenzoic acid determined ranged from the detection limit to 95 microg l(-1) urine. The method allowed the quantification of low-level internal exposure to dinitrotoluene.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
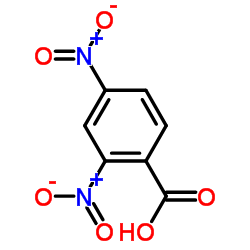 |
2,4-Dinitrobenzoic acid
CAS:610-30-0 |
C7H4N2O6 |
|
Spectrophotometric Determination of Diazepam in Pure form, T...
2007-03-01 [Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 3(1) , 50-5, (2007)] |
|
Separation and determination of perfluorinated carboxylic ac...
2006-09-22 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1128(1-2) , 290-7, (2006)] |
|
Biodegradation of the pesticide 4,6-dinitro-ortho-cresol by ...
1997-10-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48(4) , 441-8, (1997)] |
|
2-nitrobenzoate 2-nitroreductase (NbaA) switches its substra...
2013-01-01 [J. Bacteriol. 195(2) , 180-92, (2013)] |
|
Characterization of a nitroreductase with selective nitrored...
2009-11-11 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(21) , 10457-65, (2009)] |