Highly efficient antibody-catalyzed deuteration of carbonyl compounds.
Avidor Shulman, Danielle Sitry, Hagit Shulman, Ehud Keinan
Index: Chemistry 8(1) , 229-39, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Antibody 38C2 efficiently catalyzes deuterium-exchange reactions at the alpha position of a variety of ketones and aldehydes, including substrates that have a variety of sensitive functional groups. In addition to the regio- and chemoselectivity of these reactions, the catalytic rates (kcat) and rate-enhancement values (kcat/kun) are among the highest values ever observed with catalytic antibodies. Comparison of the substrate range of the catalytic antibody with highly evolved aldolase enzymes, such as rabbit-muscle aldolase, highlights the much broader practical scope of the antibody, which accepts a wide range of substrates. The hydrogen-exchange reaction was used for calibration and mapping of the antibody active site. Isotope-exchange experiments with cycloheptanone reveal that the formation of the Schiff base species (as concluded from the 16O/18O exchange rate at the carbonyl oxygen) is much faster than the formation of the enamine intermediate (as concluded from the H/D exchange rate), and both steps are faster than the antibody-catalyzed aldol addition reaction.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
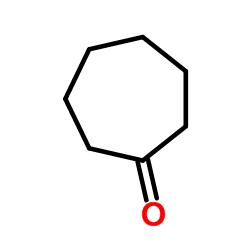 |
Cycloheptanone
CAS:502-42-1 |
C7H12O |
|
Method transfer from high-pressure liquid chromatography to ...
2015-07-03 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1401 , 52-9, (2015)] |
|
Method transfer from high-pressure liquid chromatography to ...
2014-10-03 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1362 , 206-17, (2014)] |
|
Optimization of startup and shutdown operation of simulated ...
2011-01-01 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1218(25) , 3876-89, (2011)] |
|
A straightforward route to stereodefined functionalized cycl...
2000-06-16 [J. Org. Chem. 65(12) , 3869-74, (2000)] |
|
In vitro co-metabolism of ethanol and cyclic ketones.
2002-08-15 [Toxicology 177(2-3) , 207-13, (2002)] |