| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
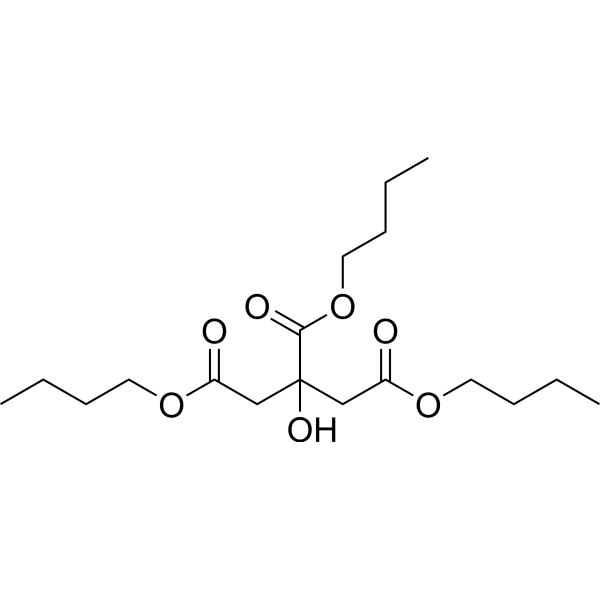 |
Tributyl citrate
CAS:77-94-1 |
|
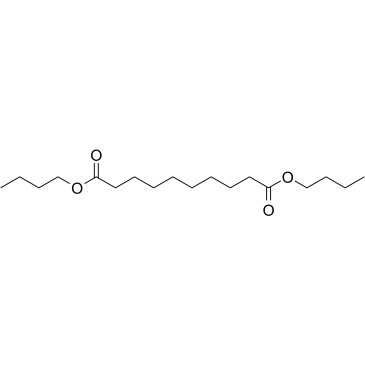 |
Dibutyl sebacate
CAS:109-43-3 |