Fragmentation behavior of poly(methyl methacrylate) during matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization.
Tomomi Iura, Hajime Ohtani
Index: Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 29(2) , 155-62, (2015)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) has been widely utilized for the structural characterization of various synthetic polymers. However, polymer sample molecules can occasionally decompose even in the MALDI process depending on the measurement conditions. In this work, the fragmentation behavior of radically polymerized poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) during laser irradiation in MALDI was investigated in detail.Two types of PMMA samples with oligomeric molar mass were examined: Sample A was synthesized with an excess content of a chain transfer reagent to form simple molecules with less labile structures. Sample B was polymerized with a greater amount of a peroxide initiator without any chain transfer reagent, which resulted in the formation of various terminal and chain structures including relatively labile ones. The original components and fragment ions for the PMMA samples were precisely assigned using a high-resolution MALDI spiral time-of-flight MS system. Electrospray ionization MS measurements were also performed for comparison.The PMMA chains underwent fragmentation during the MALDI process with high laser intensity even for the relatively stable sample A. The fragmentation reactions proceeded mainly through 1,5-hydrogen rearrangements via a six-membered intermediate structure. Furthermore, PMMA molecules formed via recombination termination in sample B selectively decomposed during the MALDI-MS measurements even with low laser intensity.It was observed that the fragmentation reactions in the PMMA chains in MALDI with high laser power were generally the same as those in the post-source decay or collision-induced dissociation in MALDI-MS/MS measurements. Even with low laser intensity, less stable structures in the PMMA chain, especially head-to-head linkages, were readily decomposed during the MALDI process. Possible fragmentation, therefore, should be considered in the structural characterization of synthetic polymer samples by MALDI-MS.Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
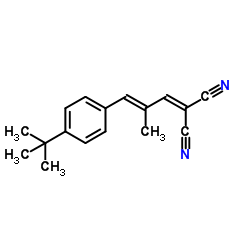 |
t-2-(3-(4-t-bu.-phenyl)-2-me-2-propenyl&
CAS:300364-84-5 |
C17H18N2 |
|
Tandem mass spectrometry and ion mobility mass spectrometry ...
2015-02-21 [Analyst 140(4) , 1182-91, (2015)] |
|
Biodegradable and biocompatible poly(ethylene glycol)-based ...
2014-09-01 [Adv. Healthc. Mater. 3(9) , 1496-507, (2014)] |
|
A novel combined micellar system of lapatinib and Paclitaxel...
2015-01-01 [J. Pharm. Sci. 104(1) , 165-77, (2014)] |
|
Exploration of cardanol-based phenolated and epoxidized resi...
2014-09-16 [Anal. Chim. Acta 843 , 46-58, (2014)] |
|
Organic-inorganic azafullerene-gold C(59)N-Au nanohybrid: sy...
2014-11-03 [Chemistry 20(45) , 14729-35, (2014)] |