The role of intermolecular interactions: studies on model systems for bacterial biofilms.
C Mayer, R Moritz, C Kirschner, W Borchard, R Maibaum, J Wingender, H C Flemming
Index: Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 26(1) , 3-16, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The mechanical stability of biofilms and other microbial aggregates is of great importance for both the maintenance of biofilm processes and the removal of undesired biofilms. The binding forces are weak interactions such as London dispersion forces, electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonds. In a first attempt to rank their contribution, the viscosity of solutions of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from a mucoid strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is measured. In order to distinguish the binding forces, substances are chosen which individually address the different types of bonds. Polyacrylic acid is identified as a suitable model system for EPS when molecular interactions are studied. Electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonds are found to be the dominating forces among macromolecules within the biofilm.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
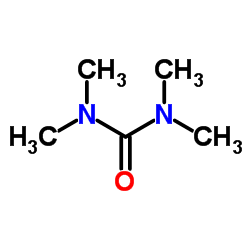 |
Tetramethylurea
CAS:632-22-4 |
C5H12N2O |
|
Transformation of NIH3T3 mouse fibroblast cells by MUC16 muc...
2015-01-01 [Int. J. Oncol. 46(1) , 91-8, (2014)] |
|
Coordination chemistry study of hydrated and solvated lead(I...
2011-02-07 [Inorg. Chem. 50(3) , 1058-72, (2011)] |
|
Solvent-induced lysozyme gels: rheology, fractal analysis, a...
2005-09-15 [J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 289(2) , 394-401, (2005)] |
|
Strong slowing down of water reorientation in mixtures of wa...
2008-03-20 [J. Phys. Chem. A 112(11) , 2355-61, (2008)] |
|
The hydrogen bond network structure within the hydration she...
2010-07-21 [J. Chem. Phys. 133(3) , 035102, (2010)] |