Molecular Epidemiology of Hospital Outbreak of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2014.
Shamsudeen F Fagbo, Leila Skakni, Daniel K W Chu, Musa A Garbati, Mercy Joseph, Malik Peiris, Ahmed M Hakawi
Index: Emerging Infect. Dis. 21 , 1981-8, (2015)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We investigated an outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) at King Fahad Medical City (KFMC), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, during March 29-May 21, 2014. This outbreak involved 45 patients: 8 infected outside KFMC, 13 long-term patients at KFMC, 23 health care workers, and 1 who had an indeterminate source of infection. Sequences of full-length MERS coronavirus (MERS-CoV) from 10 patients and a partial sequence of MERS-CoV from another patient, when compared with other MERS-CoV sequences, demonstrated that this outbreak was part of a larger outbreak that affected multiple health care facilities in Riyadh and possibly arose from a single zoonotic transmission event that occurred in December 2013 (95% highest posterior density interval November 8, 2013-February 10, 2014). This finding suggested continued health care-associated transmission for 5 months. Molecular epidemiology documented multiple external introductions in a seemingly contiguous outbreak and helped support or refute transmission pathways suspected through epidemiologic investigation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
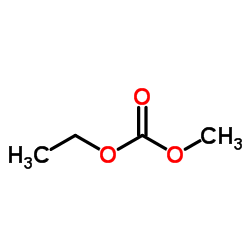 |
Ethyl-methylcarbonat
CAS:623-53-0 |
C4H8O3 |
|
Determination of ultraviolet filters in bathing waters by st...
2016-01-15 [Talanta 147 , 246-52, (2015)] |
|
Human IgG is produced in a pro-form that requires clipping o...
2015-01-01 [MAbs 7 , 672-80, (2015)] |
|
Benchmark studies of UV-vis spectra simulation for cinnamate...
2015-06-01 [J. Mol. Model. 21 , 150, (2015)] |
|
Evaluation of candidate vaccine approaches for MERS-CoV.
2015-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 6 , 7712, (2015)] |
|
Antigen-Specific Th17 Cells Are Primed by Distinct and Compl...
2015-10-01 [PLoS Pathog. 11 , e1005164, (2015)] |