| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
![2,3-Dihydrothieno[3,4-b][1,4]dithiine Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/218/158962-92-6.png) |
2,3-Dihydrothieno[3,4-b][1,4]dithiine
CAS:158962-92-6 |
|
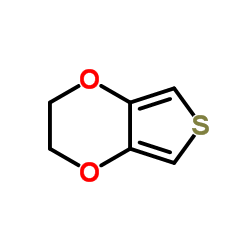 |
3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene
CAS:126213-50-1 |