Brain phospholipase C, diacylglycerol lipase and monoacylglycerol lipase are involved in (±)-epibatidine-induced activation of central adrenomedullary outflow in rats.
Takahiro Shimizu, Kenjiro Tanaka, Kumiko Nakamura, Keisuke Taniuchi, Kunihiko Yokotani
Index: Eur. J. Pharmacol. 691(1-3) , 93-102, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We previously reported that intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.) administered (±)-epibatidine (a potent agonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors) (1, 5 and 10 nmol/animal) dose-dependently elevated plasma levels of noradrenaline and adrenaline and that this response was reduced by i.c.v. administered indomethacin (cyclooxygenase inhibitor) and abolished by bilateral adrenalectomy, indicating the involvement of brain arachidonic acid, as a substrate of cyclooxygenase, in this alkaloid-induced secretion of both catecholamines from the adrenal medulla in rats. Arachidonic acid is mainly released by the action of phospholipase A(2), but is also released by a phospholipase C-, diacylglycerol lipase- and monoacylglycerol lipase-mediated pathway. In the present study, (±)-epibatidine (5 nmol/animal, i.c.v.)-induced elevation of plasma catecholamines was not influenced by pretreatment with mepacrine (phospholipase A(2) inhibitor) (1.1 and 2.2 μmol/animal, i.c.v.), but was effectively reduced by pretreatment with U-73122 (1-[6-[[(17 β)-3-methoxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-yl]amino]hexyl]-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione) (phospholipase C inhibitor) (10 and 30 nmol/animal, i.c.v.), RHC-80267 [1,6-bis(cyclohexyloximinocarbonylamino)hexane] (diacylglycerol lipase inhibitor) (1.3 and 2.6 μmol/animal, i.c.v.), MAFP (methyl arachidonoyl fluorophosphonate) (monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor) (0.7 and 1.4 μmol/animal, i.c.v.) or JZL184 [4-nitrophenyl 4-(dibenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl(hydroxy)methyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate] (selective monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor) (0.7 and 1.4 μmol/animal, i.c.v.). Immunohistochemical studies demonstrated that (±)-epibatidine (10 nmol/animal, i.c.v.) activates spinally projecting neurons expressing monoacylglycerol lipase in the rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus, a control center of central sympatho-adrenomedullary outflow. Taken together, the brain phospholipase C-, diacylglycerol lipase- and monoacylglycerol lipase-mediated pathway seems to be involved in the centrally administered (±)-epibatidine-induced activation of central adrenomedullary outflow in rats.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
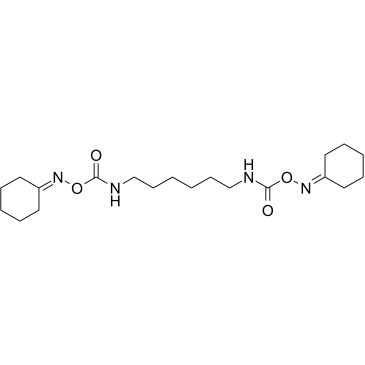 |
RHC-80267
CAS:83654-05-1 |
C20H34N4O4 |
|
Capsazepine, a vanilloid antagonist, abolishes tonic respons...
2005-03-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 288(3) , L460-70, (2005)] |
|
L- and N-current but not M-current inhibition by M1 muscarin...
2008-07-01 [J. Cell Physiol. 216(1) , 91-100, (2008)] |
|
Brain phospholipase C-diacylglycerol lipase pathway is invol...
2004-09-19 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 499(1-2) , 99-105, (2004)] |
|
Antimicrobial activity of clofazimine is not dependent on my...
2004-06-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 53(6) , 971-4, (2004)] |
|
Bidirectional roles of the brain 2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycerol ...
2008-03-17 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 582(1-3) , 62-9, (2008)] |