Improved tumor targeting and antitumor activity of camptothecin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles by preinjection of blank solid lipid nanoparticles.
Dong-Jin Jang, Cheol Moon, Euichaul Oh
Index: Biomed. Pharmacother. 80 , 162-72, (2016)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
This study aimed to enhance the in vivo antitumor effects of camptothecin (CPT), a strong antitumor agent whose delivery is limited by poor aqueous solubility and instability of the active lactone form. CPT was loaded into sterically stabilized, solid lipid nanoparticles (CPT-SLNs) formulated for intravenous administration. The influence of preinjected blank SLNs on the tumor targeting, pharmacokinetics and antitumor activity of CPT-SLNs was investigated. The CPT-SLNs composed of trilaurin-based lipid matrix containing poloxamer188 and pegylated phospholipid as stabilizers were prepared by hot homogenization method and evaluated for in vitro characteristics and in vivo performance. The CPT-SLNs showed an in vitro long-term sustained release pattern and effectively protected the CPT lactone form from hydrolysis under physiological conditions. Notable tumor targeting and tumor growth inhibition were observed after intravenous administration of CPT-SLNs to mice with subcutaneous transplants of CT26 carcinoma cells. In pharmacokinetic studies in rats, CPT-SLNs markedly elevated plasma CPT level and prolonged blood circulation compared to free CPT. Nonetheless, high uptake of CPT-SLNs by reticuloendothelial system (RES)-rich tissues resulted in limited tumor targeting of CPT-SLNs and plasma CPT levels. Preinjection of blank SLNs before administration of CPT-SLNs to tumor-bearing mice substantially reduced the accumulation of CPT-SLNs in RES organs. This led to significantly enhanced tumor targeting, improved pharmacokinetic parameters and increased antitumor efficacy of CPT-SLNs. These results suggested that the in vivo antitumor effects of CPT-SLNs could be further enhanced by preinjection of blank SLNs. Therefore, CPT-SLNs with preinjected blank SLNs could be a potential approach for stable and effective CPT-based cancer therapy. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
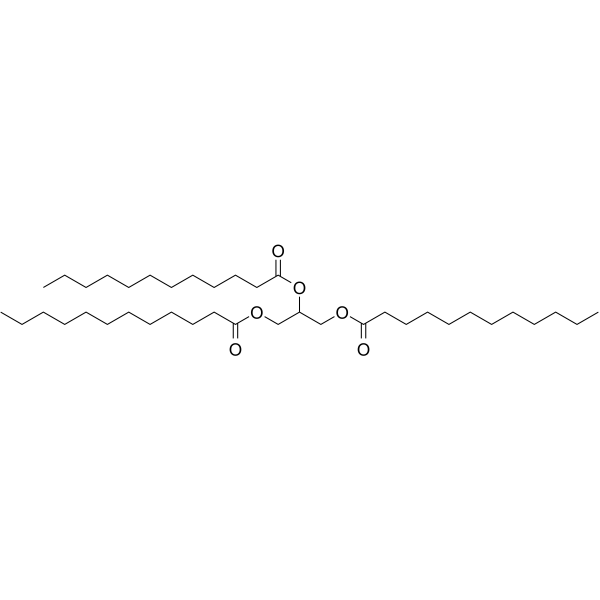 |
Trilaurin
CAS:538-24-9 |
C39H74O6 |
|
Identification of lipid- and protein-based binders in painti...
2015-01-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407(3) , 1015-22, (2015)] |
|
Surface properties of artificial tear film lipid layers: eff...
2014-07-01 [Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(7) , 4448-54, (2014)] |
|
Cyclosporin nanosphere formulation for ophthalmic administra...
2012-11-01 [Int. J. Pharm. 437(1-2) , 275-6, (2012)] |
|
Saturated triglycerides and fatty acids activate neutrophils...
2002-04-01 [Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 32(4) , 285-9, (2002)] |
|
Myristate is selectively incorporated into surfactant and de...
2010-11-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 299(5) , R1306-16, (2010)] |