| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
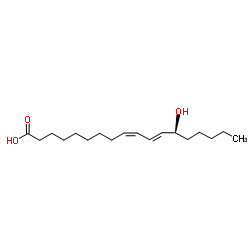 |
13S-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid
CAS:29623-28-7 |
|
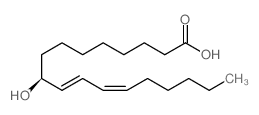 |
9(S)-HODE
CAS:73543-67-6 |