| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
4-Bromophenol
CAS:106-41-2 |
|
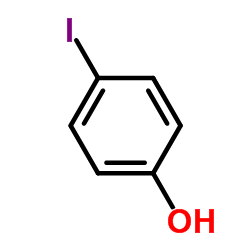 |
4-Iodophenol
CAS:540-38-5 |
|
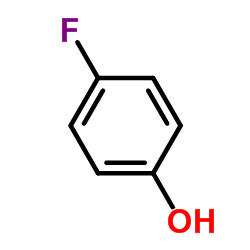 |
4-Fluorophenol
CAS:371-41-5 |
|
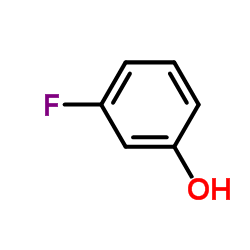 |
3-Fluorophenol
CAS:372-20-3 |