A synthetic emulsion reproduces the functional properties of pulmonary surfactant.
D J McIver, F Possmayer, S Schürch
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 751(1) , 74-80, (1983)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
An effective substitute for pulmonary surfactant must be able to reduce water-vapour surface tensions to under 1 mN/m and it must spread rapidly and spontaneously at the air interface from the aqueous phase. Pure dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine meets the former requirement, but not the latter. A synthetic surfactant is described which meets both of these criteria. The surfactant is prepared as a DPPC monolayer stabilizing an aqueous emulsion of an inert fluorocarbon oil; it spreads rapidly at the air/liquid interface, lowers the surface tension to under 1 mN/m during compression at the air/liquid interface and restores normal pressure-volume characteristics to surfactant-depleted lungs.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
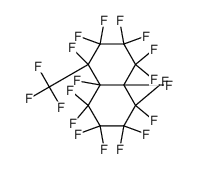 |
Perfluoro(Methyldecahydronaphthalene)
CAS:51294-16-7 |
C11F20 |
|
The aerobic oxidation of alcohols with a ruthenium porphyrin...
2008-06-07 [Org. Biomol. Chem. 6(11) , 1961-5, (2008)] |
|
[Biological fixation of nitrogen and growth of bacteria of t...
2007-01-01 [Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 43(4) , 443-9, (2007)] |
|
[Effect of perfluorodecalin, carbogal, and perfluoromethylde...
2006-01-01 [Mikrobiologiia 75(3) , 371-6, (2006)] |
|
Synthesis of composite emulsions and complex foams with the ...
2007-10-01 [Small 3(10) , 1792-802, (2007)] |
|
Perfluoro-1-methyldecalin as a potential oxygen carrier with...
1985-06-01 [Curr. Eye Res. 4(6) , 732-3, (1985)] |