| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Camalexin
CAS:135531-86-1 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
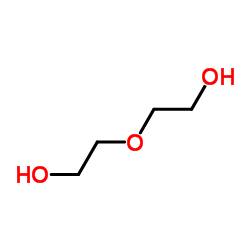 |
Diethylene glycol
CAS:111-46-6 |